Health & Medicine
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGetting drugs into the brain is hard. Maybe a parasite can do the job
Researchers want to harness the parasite that causes toxoplasmosis to ferry drugs, but some question if the risks can be eliminated.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA new algae-based menstrual pad could stop leaks
By turning period blood into a gel, the pad’s alginate powder filler reduces leakage.
By Claire Yuan -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSepsis tests take days, putting patients at risk. A new method may cut wait time
A faster way to figure out what bacteria is causing a potentially deadly bloodstream infection could let doctors treat it more quickly and efficiently.
By Claire Yuan -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHIV prevention may only require two injections per year
There were no new HIV infections among adolescent girls and young women taking a new PrEP formulation, a twice-yearly shot of the drug lenacapavir.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSome melanoma cancer cells may punch their way through the body
A new study clarifies how melanoma cells use cell membrane protrusions called “blebs” to burrow through tissue.
By Claire Yuan -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow to stay healthy during the COVID-19 summertime surge
Infections peak in the summer and winter. Up-to-date vaccinations, testing and masking can slow the spread.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe odds of developing long COVID dropped as the coronavirus evolved
As different coronavirus variants took center stage during the pandemic, the chances of developing long COVID fell, especially for vaccinated people.
-
 Neuroscience
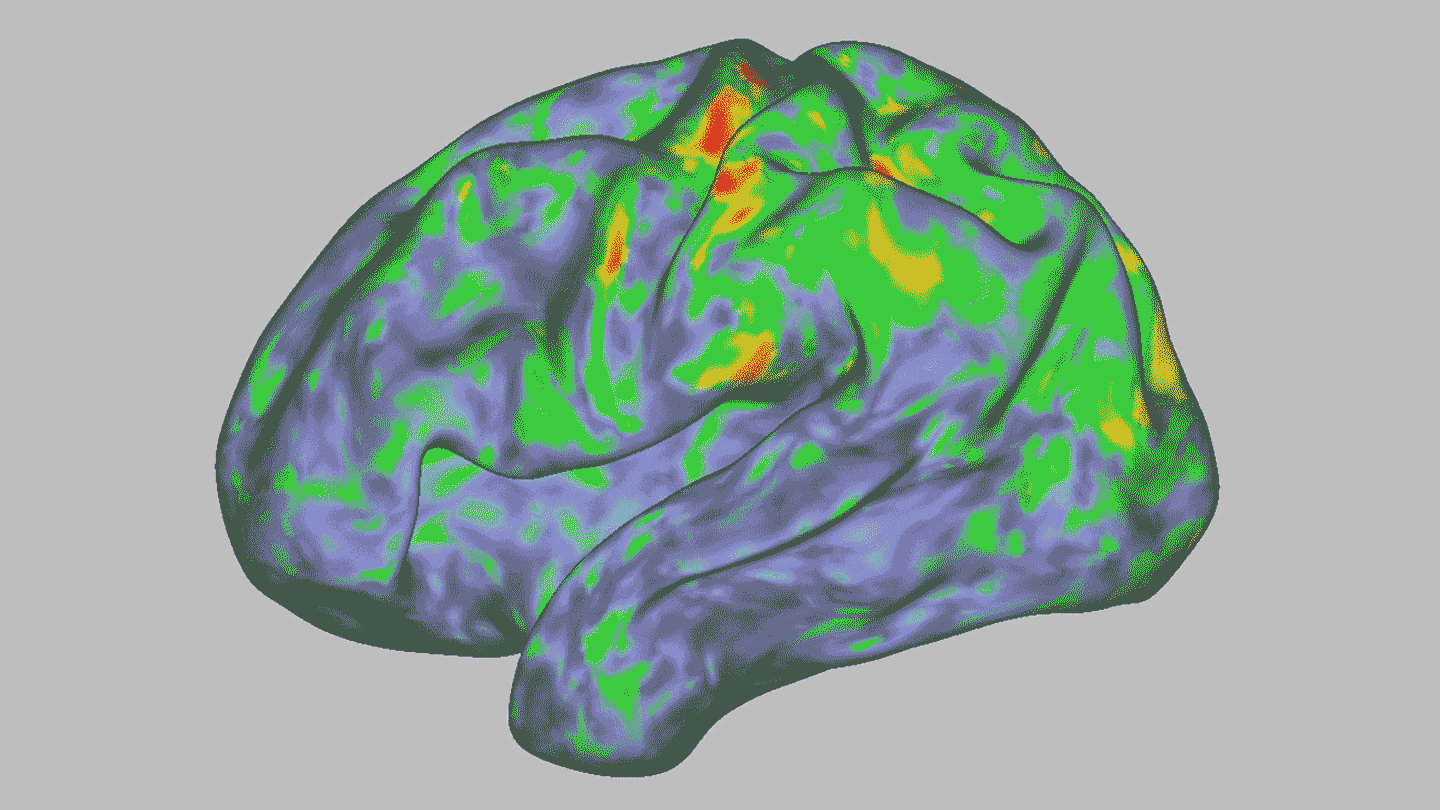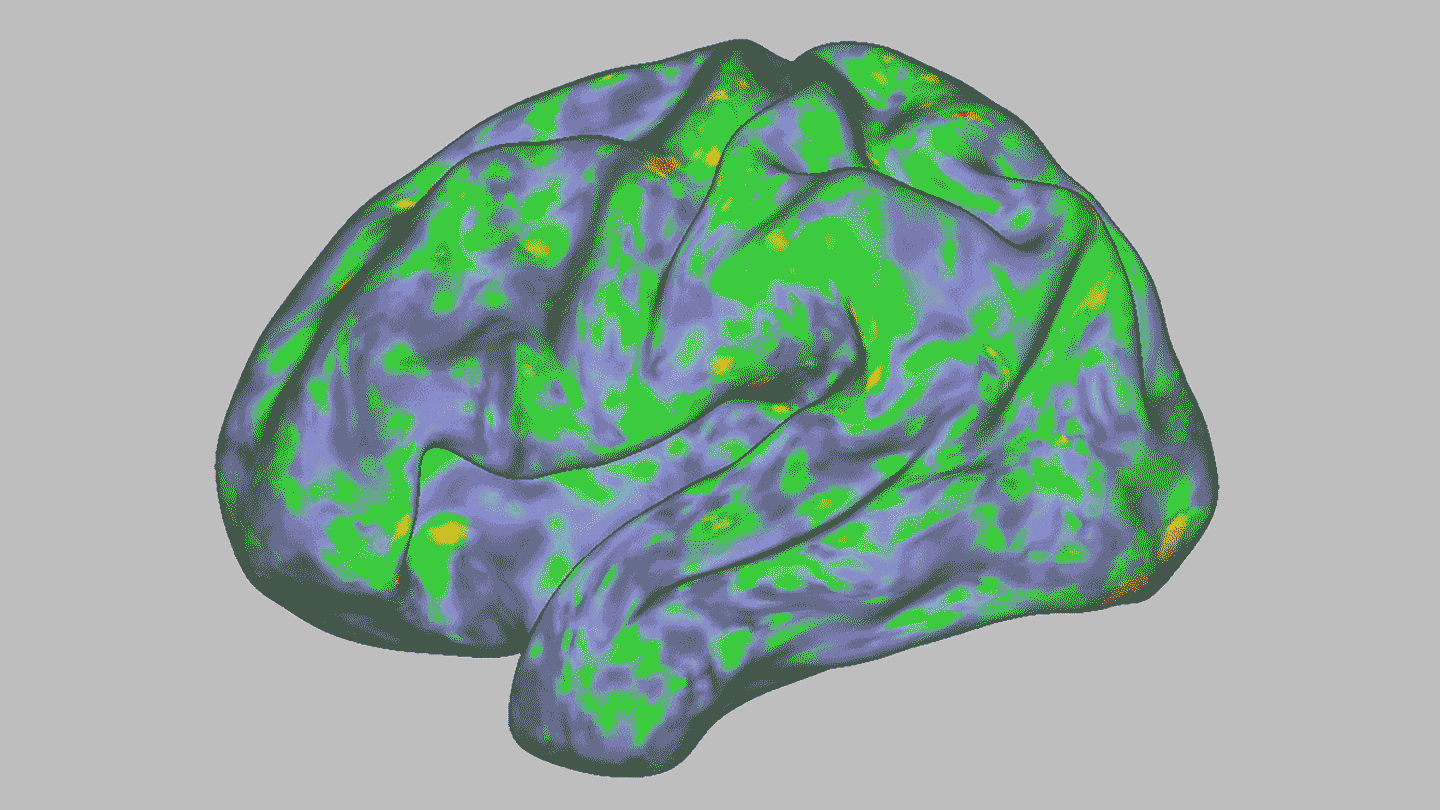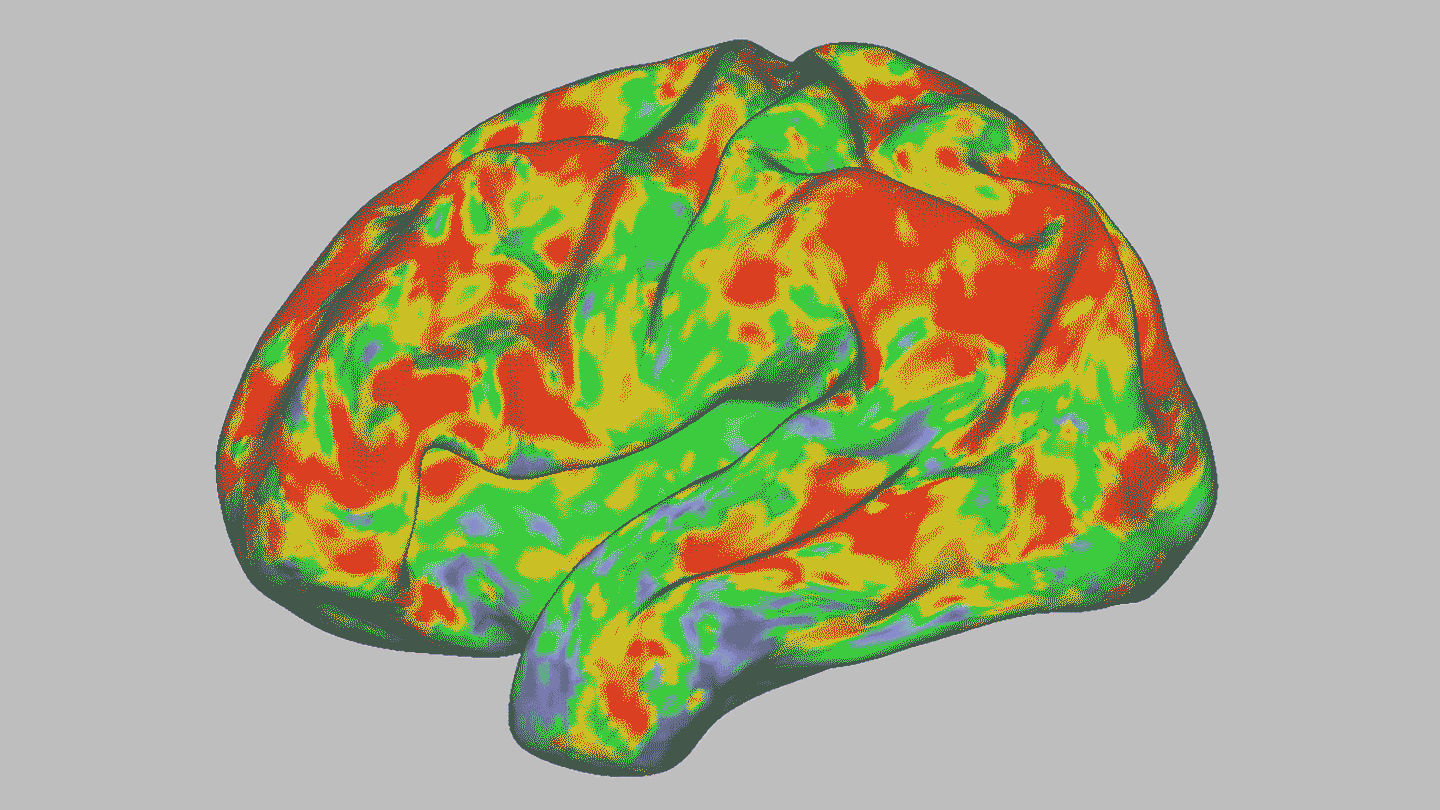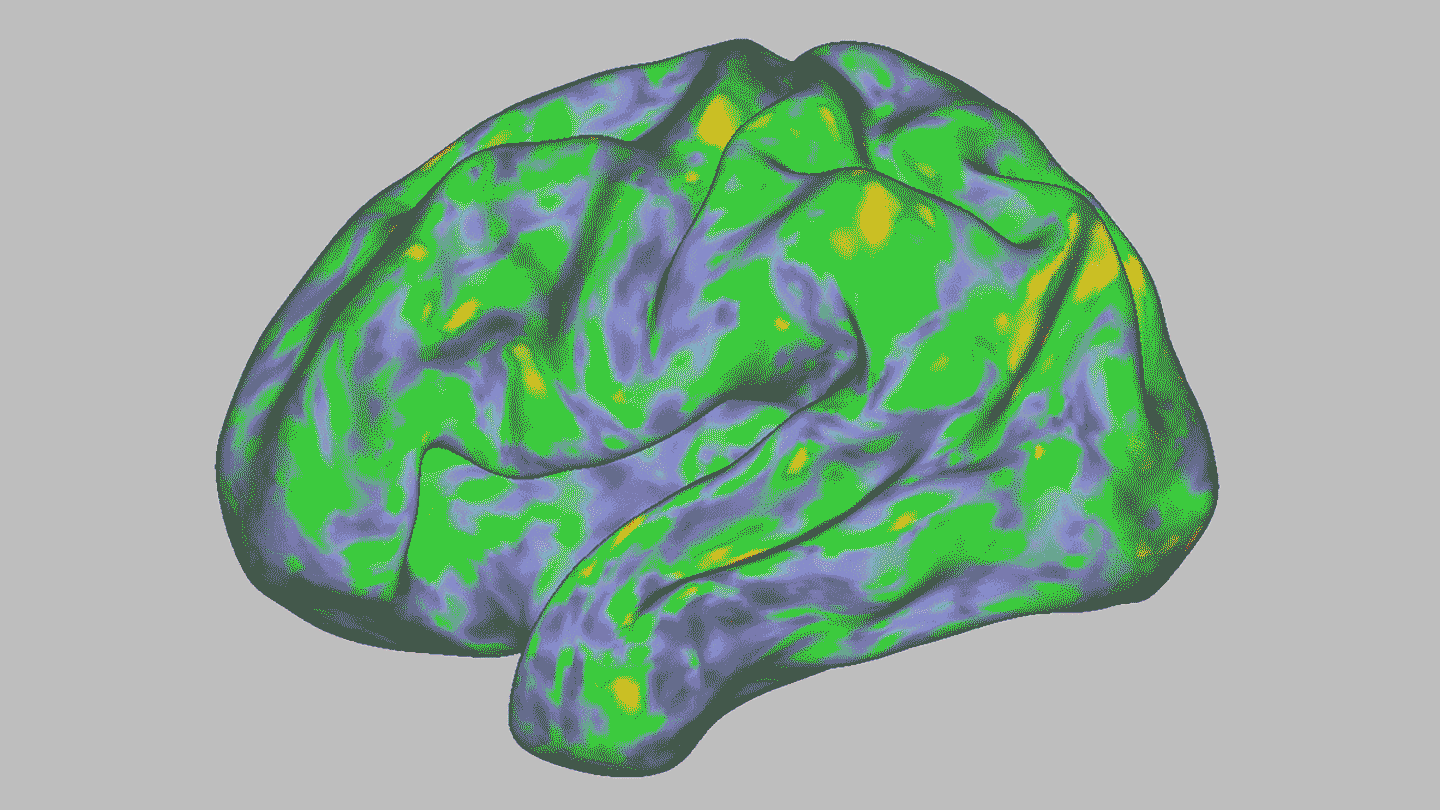
NeurosciencePsilocybin temporarily dissolves brain networks
A high dose of the psychedelic drug briefly throws the brain off kilter. Other, longer-lasting changes could hint at psilocybin's therapeutic effects.
-
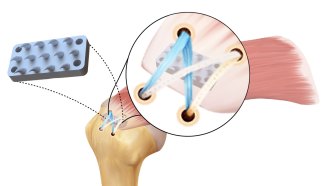 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThis python-inspired device could make rotator cuff surgeries more effective
A new device, modeled after a python’s teeth and grip, could double the strength of rotator cuff repairs and prevent retearing after surgery.
By Claire Yuan -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRogue antibodies may cause some long COVID symptoms
Tissue-targeting antibodies have been a key suspect in long COVID. Now, two studies show that antibodies from patients can cause symptoms in mice.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBird flu has been invading the brains of mammals. Here’s why
Although H5N1 and its relatives can cause mild disease in some animals, these viruses are more likely to infect brain tissue than other types of flu.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBreastfeeding should take a toll on bones. A brain hormone may protect them
The hormone CCN3 improves bone strength even as breastfeeding saps bones of calcium, a study in mice shows.
By Claire Yuan